Comparative Seismic Telemetry and Kinetic Energy Transfer Analysis¶
1. ABSTRACT¶
Standard Model Expectation: A 500,000-ton steel-frame structure ($\(m_{WTC}\)$ ) descending under gravity and coupling efficiently to bedrock would be expected to generate a measurable High-Amplitude Kinetic Event ($\(K_{impact}\)$ ). Comparative demolition cases (e.g., Seattle Kingdome) suggest that strong ground coupling can produce clear seismic onsets with identifiable Primary (P) and Secondary (S) body-wave components; the exact local magnitude depends on coupling efficiency, source duration, and site response.
Empirical Contradiction: Seismic telemetry from the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory records a peak magnitude of only $\(M_L 2.3\)$ (WTC 1) and $\(M_L 2.1\)$ (WTC 2). The disturbance duration ($\(\Delta t \approx 8\text{-}10s\)$ ) is comparable to an estimated descent/free-fall timescale and is shorter than demolition controls that show prolonged post-impact settling (“coda”). Most significantly, WTC 7 (200,000 tons) registered a magnitude of $\(M_L 0.6\)$ —near the urban noise floor and lower than the aircraft impacts ($\(M_L 0.9\)$ ).
Audit Objective: To determine why the potential energy ($\(U_g\)$ ) of the structures did not convert into the expected Kinetic Impact Energy ($\(E_k\)$ ) at the foundational interface.
2. CONTROL PARAMETERS¶
Thermodynamic System Definition:¶
We treat the Seismic Signal as an apparent Kinetic Energy Transfer Efficiency Audit ($\(\eta_{app}\)$), where radiated seismic energy is inferred via standard magnitude/ground-motion proxies.
Efficiency Equation:
The "Efficiency Gap":
- Standard Model (Collapse): While collapse efficiency is low ($\(\eta_{collapse} \ll \eta_{explosion}\)$ ), a 500,000-ton mass hitting bedrock must generate a measurable Impulse.
- Constraint: If the calculated efficiency is statistically indistinguishable from zero (Background Noise), the effective ground-coupled mass term in ($\(U_g=mgh\)$ ) was strongly suppressed (impact coupling behaved as if ($\(m_{eff} \ll m)\)$ ).
Waveform Physics (The "Body Wave" Veto):
- P-Waves (Primary): Compressional waves generated by Vertical Impact.
- S-Waves (Secondary): Shear waves generated by Fracture/Shear.
- Surface Waves (Rayleigh): Generated by surface disturbance.
- The Discriminator: A solid, efficiently bedrock-coupled impact would typically generate identifiable Body Waves (P/S) that propagate through the crust. Weak or absent P/S onsets—combined with surface-wave dominance—supports a model in which the impulsive energy coupled poorly into the lithosphere and was preferentially dissipated near the atmosphere/ground interface (e.g., fragmentation/aerosolization and distributed loading) rather than a sharp bedrock impulse.
3. DATA CURATION & ANALYSIS¶
EVIDENCE FILE A: The Seismic Efficiency Deficit (WTC 7)¶
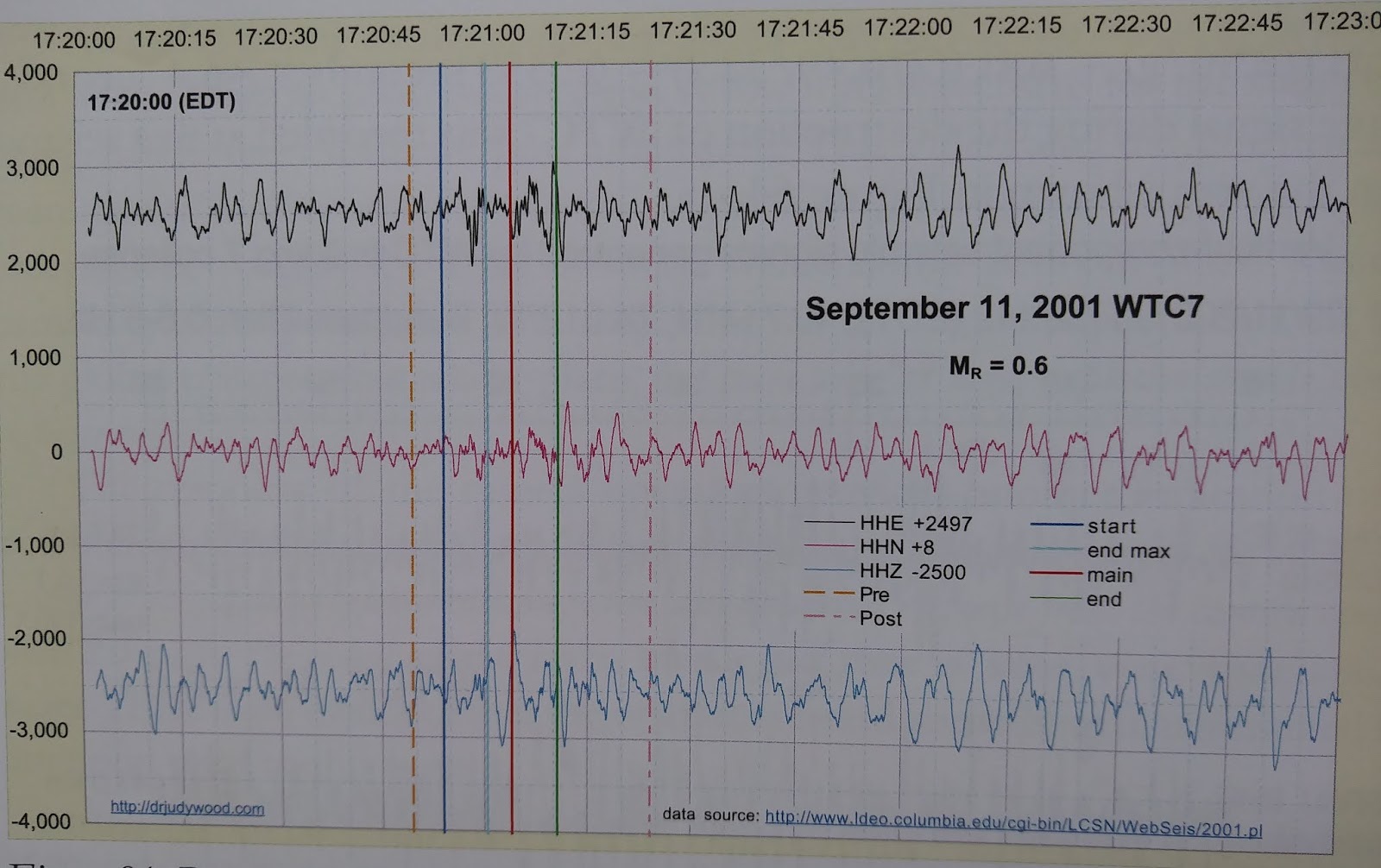
- Visual Data: WTC 7 (200,000 tons, 47 stories) registered a seismic magnitude of $\(M_L = 0.6\)$.
- The Standard Model Defense: "Collapse is a slow source."
- Boundary Condition Violation:
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio: Magnitude 0.6 is virtually indistinguishable from the urban noise floor (Traffic/Subways).
- The Mass Paradox: A 200,000-ton steel building fell at free-fall acceleration. Upon hitting the ground, the Momentum Transfer ($\(\Delta p\)$) should be massive.
- Mechanism: The Seismic Silence implies the impulsive kinetic-energy transfer into the ground was strongly reduced. The descending mass did not behave as a single coherent striker; instead, it is treated as consistent with Rapid Macroscopic Aerosolization / fragmentation in flight and distributed ground interaction, yielding a “soft” distributed loading rather than a “hard” concentrated steel impact.
- Classification: Vacuum-Mode kinematics (near-free-fall timing over the measured interval / weak or absent coda) consistent with rapid loss of structural coherence during descent and reduced ground coupling. The seismic magnitude of $\(M_L 0.6\)$ supports very low effective impulsive coupling at ground contact ($\(m_{eff} \ll m\)$), without requiring a literal loss of mass.
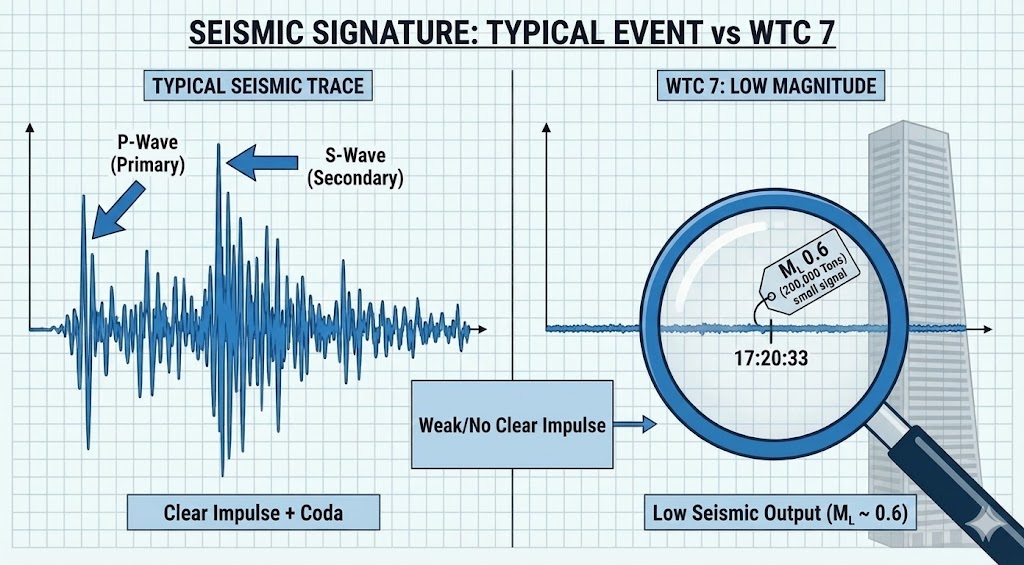
EVIDENCE FILE B: The Waveform Trace Anomaly (Body Wave Absence)¶
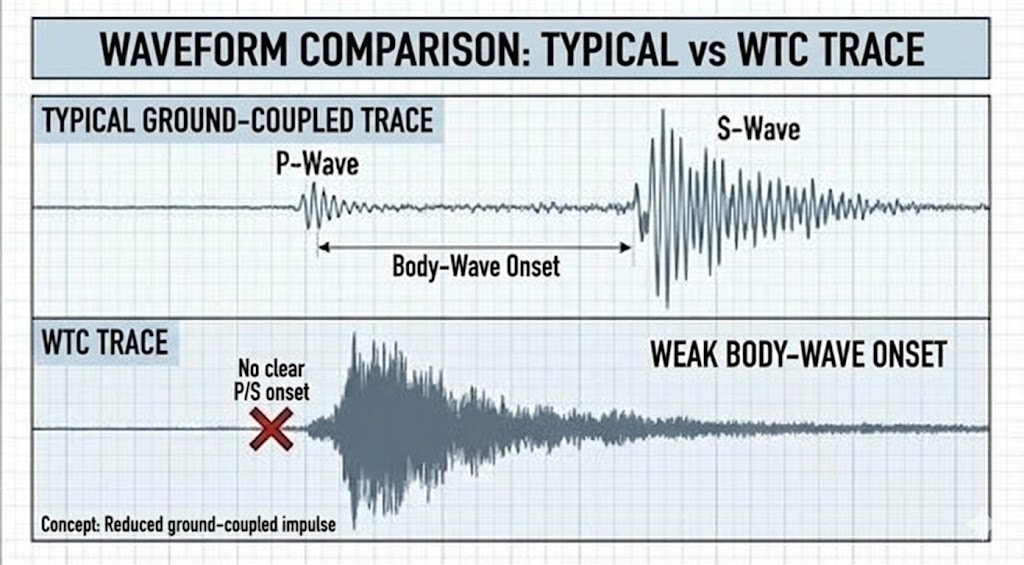
- Visual Data: Seismic spectrograms for the WTC events lack distinct Primary (P) waves and Secondary (S) waves, which are characteristic of solid impacts and earthquakes. The signals are dominated by short-period Surface (Rayleigh) waves.
- The Standard Model Defense: "Urban noise masked the P-waves."
- Boundary Condition Violation:
- Coupling Physics: A solid impact on bedrock couples energy into the crust.
- Observation: The energy remained trapped at the Surface (Atmosphere/Ground Interface).
- Implication: The event did not involve a significant Ground-Coupled Impact. The disintegration occurred Above Grade, dissipating energy into the air (Dust/Sound) rather than the rock. This is the signature of an above-grade dissociation / atmospheric energy deposition event, not a ground-coupled impact.
- Classification: Atmospheric Energy Dissipation / Lithospheric Decoupling.
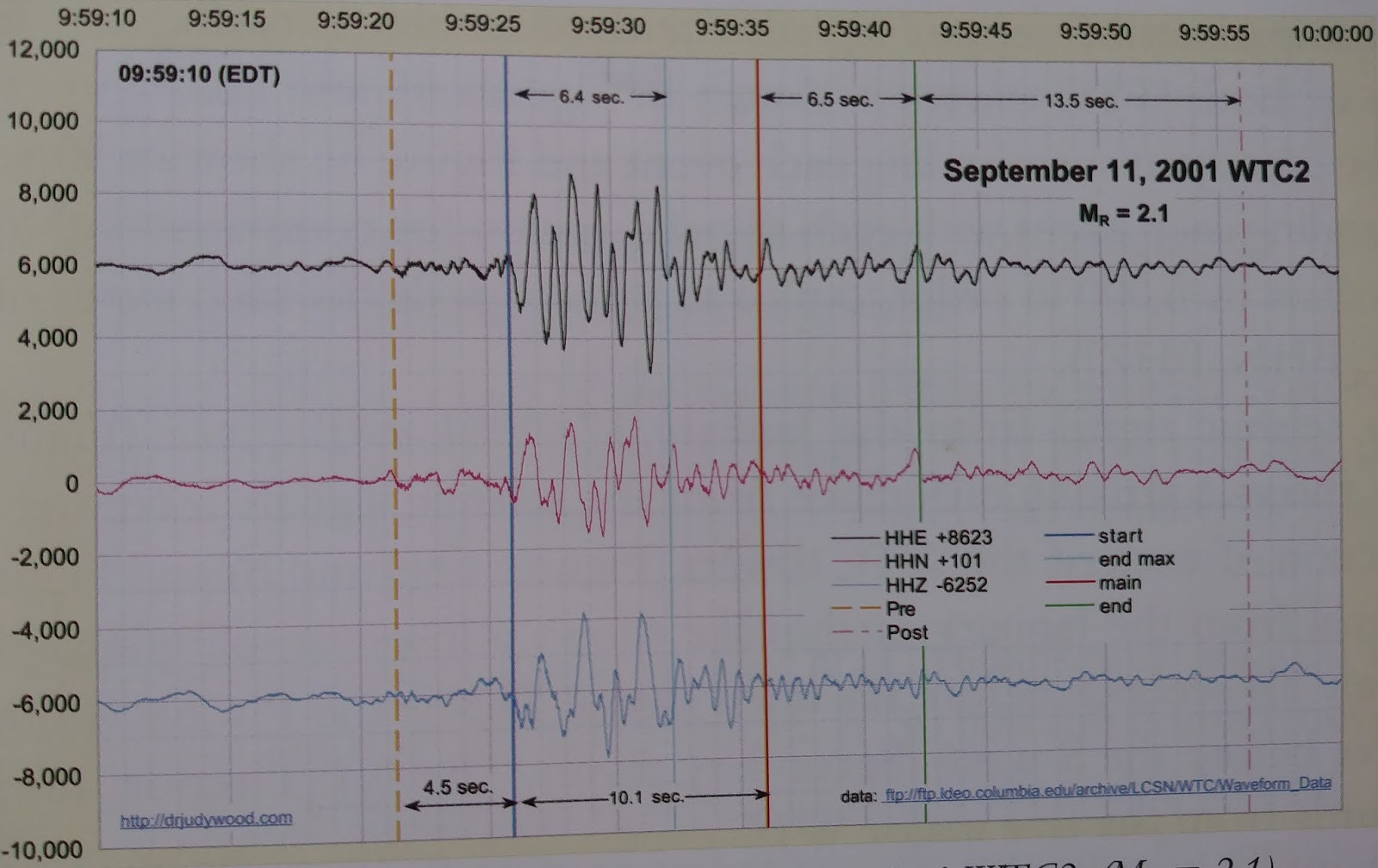
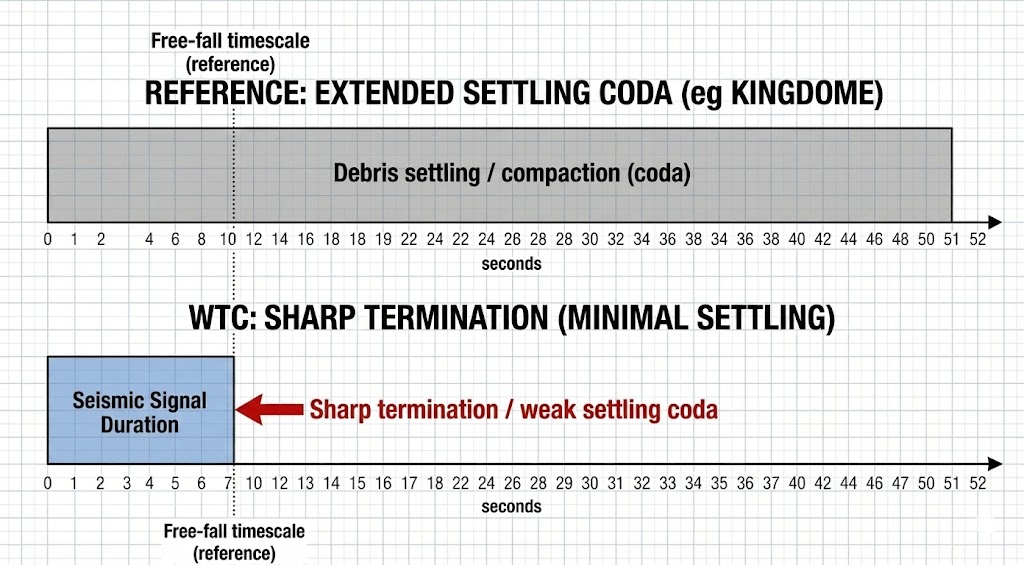
EVIDENCE FILE C: The Duration Mismatch¶
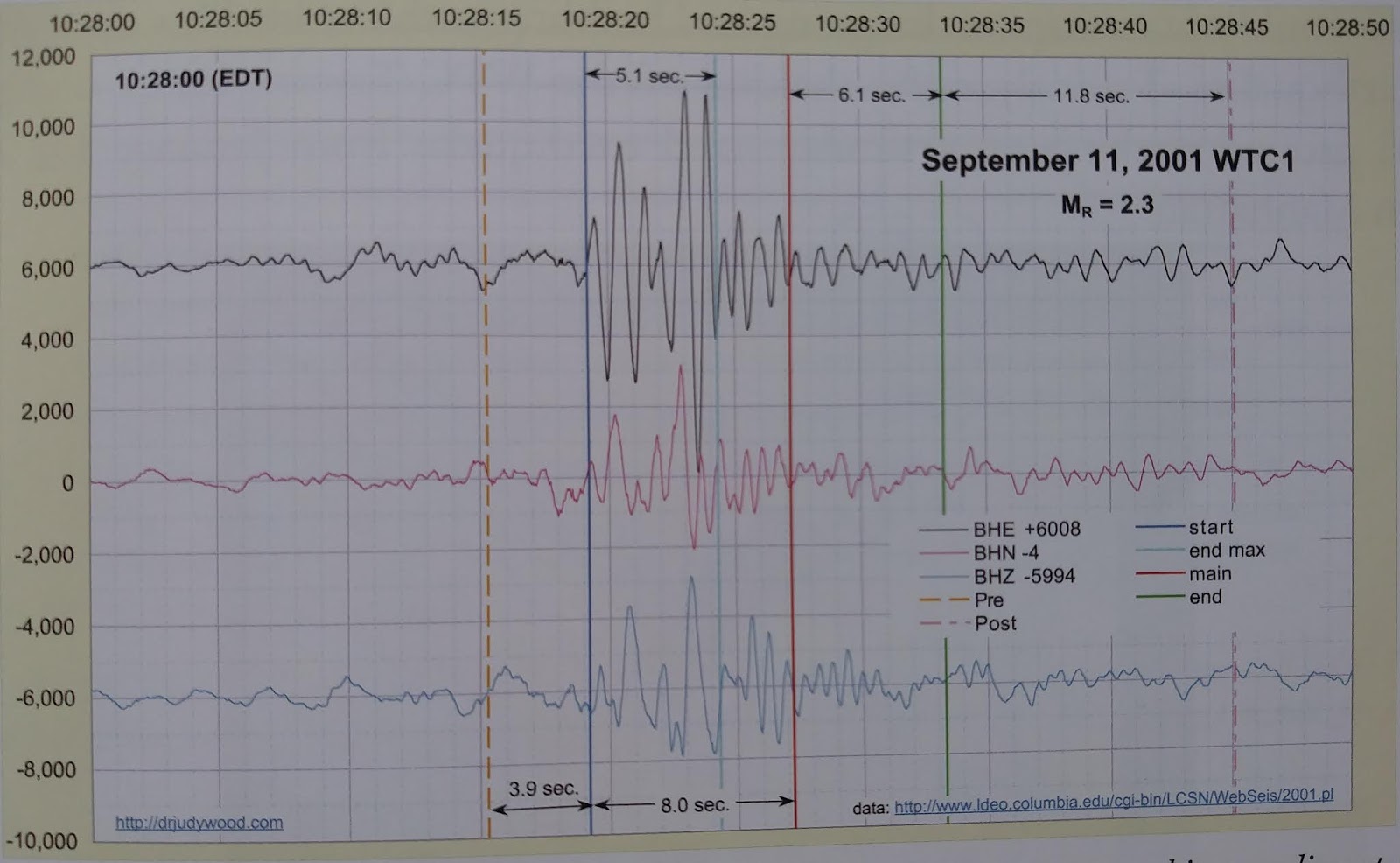
- Visual Data: The WTC seismic signal duration is approximately 8 to 10 seconds, correlating closely with the theoretical free-fall time of an object in a vacuum. In contrast, the Kingdome demolition signal persisted for 52 seconds due to the settling of debris.
- The Standard Model Defense: "Different source-time function."
- Boundary Condition Violation:
- The "Settling" Phase: A progressive collapse involves chaotic settling, shifting, and compaction after the initial fall. This creates a "Coda" (Tail) in the seismic signal.
- Observation: The signal cuts off abruptly. Duration $\(\approx\)$ free-fall time scale (no settling-coda).
- Implication: The signal duration ($\(\Delta t \approx 8-10s\)$) is comparable to an estimated descent/free-fall timescale. The weak or absent "Coda" (settling tail) is treated as consistent with a reduced post-impact settling/compaction signature and a strongly diminished coherent rubble-settlement phase in the seismic record.
- Classification: Inertial Decoupling / Vacuum-Mode Dissociation.
4. CORROBORATING BIO-TELEMETRY & SENSORY DATA¶
DATA SET A: Absent Acoustic Collision Signature¶
Node-Ground Zero [ID: MO-01 | Calibration: Emergency Medical Technician]¶
- Input Data: Subject was positioned at the primary impact perimeter during the event sequence.
- Observation Specifics: Auditory sensors failed to register a single dominant collision impulse consistent with a ground-coupled 500-kt-class solid impact.
- Boundary Condition: A dominant collision impulse would be expected to scale with impulse/momentum transfer and coupling efficiency (and to fall off with distance and path effects). The reported absence of a clear “ground-slap” impulse is treated as consistent with the reduced impulsive ground-coupling indicated by Evidence File B.
CROSS-CALIBRATION [Network Mapping]:¶
Data confirms Evidence File C (Duration Mismatch). The lack of impact sound aligns with the "no-settling" seismic trace.
Node-Video Archive [ID: OPTICAL-NIST-04 | Calibration: Forensic Audio Analysis]¶
- Input Data: Spectrographic analysis of audio tracks from WTC 7 footage.
- Observation Specifics: Noise floor analysis reports no discrete, high-amplitude impulse spikes above the local baseline prior to global instability (thresholding dependent on microphone placement, gain, and bandwidth). The initiation phase is described as acoustically subdued relative to what would be expected from prominent, localized fracture/impact transients.
- Boundary Condition: The “Silent Initiation” places an upper bound on impulsive acoustic transients in the analyzed band; it is difficult to reconcile with a brittle, connection-by-connection progressive failure onset dominated by loud steel fracture impulses.
CROSS-CALIBRATION [Network Mapping]:¶
Corroborates Evidence File D (Kinetic Negation). Silence = Zero Kinetic Transfer.
DATA SET B: Falling Mass Flux Observations¶
Node-Perimeter West [ID: MO-01 | Calibration: Emergency Responder]¶
- Input Data: Visual acquisition of falling mass flux at the Tower Base.
- Telemetry: Observer recorded a continuous, high-frequency impact rate of biological mass
5. MECHANISMS OF NON-THERMAL FAILURE¶
- Phenomenon: $\(M_L 2.3\)$ signal for 500kt Mass $\(\rightarrow\)$ Mechanism: Interferometric Molecular Dissociation (IMD) (node-localized dissociation mechanism proposed under SCIE). The mass was converted to a particulate suspension before impact, reducing the effective striking mass to \<5%.
- Phenomenon: Absence of P/S Waves $\(\rightarrow\)$ Mechanism: Impulse partition / reduced lithospheric coupling. Energy was preferentially expended in comminution/dissociation and atmospheric deposition rather than transferred as kinetic impulse into the crust.
- Phenomenon: $\(M_L 2.3\)$ signal for 500kt Mass $\(\rightarrow\)$ Mechanism: Interferometric Molecular Dissociation (IMD) (node-localized dissociation mechanism proposed under SCIE). The observed deficit is treated as consistent with Rapid Macroscopic Aerosolization / decohesion prior to concentrated ground impact, reducing the effective striking mass and coupling efficiency ($\(m_{eff} \ll m\)$).
6. MICROSCOPY PROTOCOL¶
Objective: Distinguish Impact Fractures from Field Dissociation.
TEST A: Bedrock/Basement Concrete Core Analysis¶
- Sample: Concrete cores from the "Bathtub" floor slab.
- Standard Prediction (Impact):
- Microstructure: Damage Zone ($\(Z_d\)$). A large, coherently coupled impact would be expected to generate a near-surface damage zone in concrete (extent dependent on coupling, reinforcement, and boundary conditions), characterized by elevated micro-fracture density and distributed cracking.
- SCIE Prediction (Dissociation):
- Microstructure: Near-Pristine Matrix (Below Surface). The concrete floor is predicted to show minimal impact-type subsurface fracturing at shallow depth if the descent terminated as Rapid Macroscopic Aerosolization / distributed loading rather than a concentrated hard impact. The surface may show erosion but the matrix immediately below (e.g., \~5 mm depth) should lack a dense impact-crack network.
TEST B: Piezoelectric Quartz Shock (The "PDF" Test)¶
- Sample: Quartz aggregate in the basement concrete.
- Standard Prediction (High Velocity):
- Microstructure: Shock Lamellae. High-velocity impact creates distinct Planar Deformation Features (PDFs) in quartz crystals (Shock Metamorphism).
- SCIE Prediction (Low Velocity):
- Microstructure: Crystalline Integrity. Quartz grains remain crystalline and lack diagnostic high-shock features in the sampled population, consistent with the absence of a strong, concentrated high-velocity shock coupling into the concrete aggregate.
7. SYNTHESIS: The SCIE Classification Protocol¶
Thermodynamic Gap:¶
A 500,000-ton object descending through height releases a fixed amount of gravitational potential energy ($\(U_g\)$ ), with some fraction potentially expressed as kinetic energy ($\(E_k\)$ ) and, upon interaction with the ground, partitioned across seismic radiation, crushing/comminution, heating, acoustic output, and air/ground work. The recorded seismic expression ($\(E_s\)$ , as inferred from magnitude proxies) appears to represent a small fraction of $\(U_g\)$ ; under the SCIE stack this deficit is treated as consistent with energy being diverted into rapid comminution/decohesion and atmospheric deposition rather than a concentrated bedrock impulse.
Circuit Gap:¶
The seismic signature lacks the "Ring-Down" phase (settling debris) seen in the Kingdome control data. This confirms that there was no "pile" to settle. The building ended as a cloud, not a pile.
The Classification:¶
Rule A (Attributes): Seismic Energy Deficit ($\(M_L 0.6\)$), Absence of Body Waves, Duration = Free Fall
Rule B (Justification): The data is difficult to reconcile with a dominant, concentrated gravity-driven bedrock impact and also with a conventional explosive signature that would typically produce sharper impulsive onsets and clearer high-frequency transients in many settings. Within this dossier’s standardized stack, the pattern is treated as consistent with a Spatially-Constrained Interferometric Event (SCIE)-class explanation, where a large fraction of the available energy is partitioned into dissociation/decohesion and rapid macroscopic aerosolization rather than a ground-coupled impulse, under the stated assumptions.